Menghitung Tekanan Tanah Aktif dan Pasif (Gravity Wall)
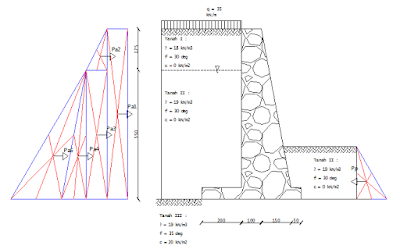
Dengan adanya perbedaan elevasi tanah maka tentunya suatu dinding penahan tanah akan mengalami gaya tekanan dari tanah, baik tekanan aktif maupun pasif. Maka, setelah menghitung berat sendiri dinding penahan tanah, langkah selanjutnya adalah menggambar tekanan tanah aktif dan pasif seperti di bawah ini : Sebelum kita hitung nilai tekanan tanah aktif maupun tekanan tanah pasifnya, terlebih dahulu kita harus menghitung koefisien tekanan tanah aktif dan pasif. Perhitungannya sebagai berikut : karena tanah I dan II nilai kohesi (c) = 0, maka rumus yang digunakan : Nilai Ka dan Kp sudah dihitung, maka selanjutnya kita hitung Tekanan tanah aktif dan pasif masing-masing bidang. <<<Sebelumnya | Selanjutnya>>>


Comments